In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrency, Bitcoin stands as a colossus, having introduced the world to the concept of digital currency. However, its journey is not without significant challenges. A critical issue currently facing Bitcoin is the "Bitcoin Trilemma," a term that encapsulates the dilemma of balancing security, scalability, and decentralization. This trilemma is becoming increasingly prominent as Bitcoin evolves, raising questions about its long-term sustainability and viability.
Understanding the Bitcoin Trilemma
In computing, the Two Generals' Problem is a thought experiment meant to illustrate the pitfalls and design challenges of attempting to coordinate an action by communicating over an unreliable link. Satoshi Nakamoto attempted solve this issue through creation of a decentralized blockchain network operating on a proof of work mechanism, see footnotes. However, the future of this network has it's own trilemma, with the idea that one can only solve 2 out of 3. It involves three key aspects:
- Security: The ability of the network to protect itself against attacks, fraud, and other threats.
- Scalability: The network's capacity to handle large numbers of transactions efficiently.
- Decentralization: Maintaining a distributed network where no single entity has control.
The Security Concern
At the heart of Bitcoin's security issue is the diminishing incentive for miners. Initially, miners were motivated by substantial BTC rewards. However, due to Bitcoin's halving schedule, these rewards are decreasing over time. This decline could eventually lead to a point where the value of rewards does not justify the effort and cost of mining, potentially compromising the security of the network.
The Scalability Dilemma
As Bitcoin's popularity grows, so does the number of transactions. The on-chain transaction processing capacity of the bitcoin network is limited by the average block creation time of 10 minutes and the original block size limit of 1 megabyte. This limitation leads to increased transaction fees and slower processing times, hindering Bitcoin's usability as a daily transaction medium.
Furthermore, energy costs are related to the bitcoin price per coin. The more valuable Bitcoin, the higher the mining costs. Current energy consumption is in the order of a large country.
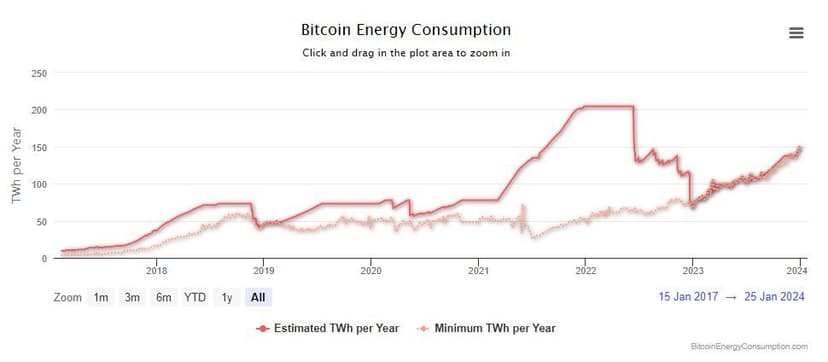 bitcoin energy consumption over time
bitcoin energy consumption over timeDecentralization at Stake
Decentralization is a foundational principle of Bitcoin, ensuring that no single entity can control the network. However, as solutions to the scalability and security issues are sought, there's a risk that the network could become more centralized, undermining one of its core values.
 BTC Nakamoto Coefficient and decentralization
BTC Nakamoto Coefficient and decentralizationPotential Solutions
Experts and enthusiasts have proposed several solutions to address the Bitcoin Trilemma:
- Increasing Transaction Fees: This approach involves compensating the decrease in mining rewards with higher transaction fees. While this could maintain miner incentives, it could also lead to higher costs for users.
- Removing the Hard Cap: Altering Bitcoin's supply limit and halving schedule could provide a more consistent reward for miners. However, this solution is controversial as it goes against Bitcoin's original design.
- Proof-of-Stake Transition: Switching to a proof-of-stake model could align miners' economic interests with the network's security. However, this shift is a significant departure from Bitcoin's current proof-of-work model.
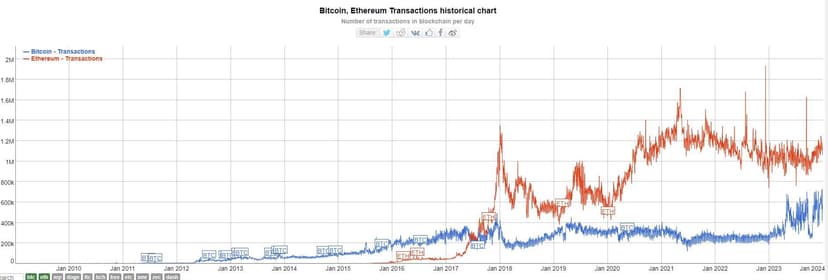 proof of work versus proof of stake transactions per day
proof of work versus proof of stake transactions per dayThe Road Ahead
The path forward for Bitcoin is fraught with challenges and uncertainties. While increasing transaction fees seems the most likely solution, it risks alienating average users due to higher costs. On the other hand, altering Bitcoin's fundamental principles could erode trust in the system.
The future of Bitcoin might depend on finding innovative solutions that balance these three aspects of the trilemma. Whether Bitcoin can adapt and overcome these challenges remains an open question. What is clear, however, is that the decisions made today will shape the future of not just Bitcoin, but the entire landscape of digital currency.
References
Bitcoin whitepaper: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
Bitcoin realtime and historic metrics; https://bitinfocharts.com/comparison/bitcoin-confirmationtime.html#3y
Two generals problem: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two_Generals%27_Problem